Deffinition and Description
Complément :
See this video
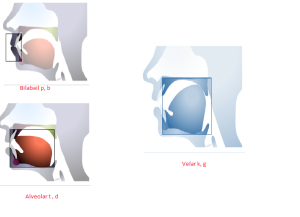
Définition : Plosives: Oral stops
They are consonants where
The air is stopped completely in the oral cavity for a brief period.Then it explodes with the release of the closure, producing loud-enough noise to be heard.
A plosive is a consonant articulation with the following characteristics:
One articulator is moved against another so as to form a stricture that allows no air to escape from the vocal tract . The stricture is then total.
After the stricture has been formed, it is released, the air is allowed to escape.
When the plosive is released the escape of air will produce a noise, loud enough to be heard. This noise is called plosion – a burst of noise.
Four phases of articulation
Closing phase
Compression phase
Release phase
Post release phase
Description of Plosives
Initial position (c v)
Closing phase
P, t, k (No voicing takes place)
b , d , g (No voicing takes place
Compression phase
P , t , k (No voicing takes place)
b , d , g (voicing takes place during the entire compression phase)
Release phase
p , t , k (Release of p,t,k is followed by an audible plosion)
b , d , g (Release of b,d,g is followed by a weak plosion)
Post-release phase
p , t , k (Air escapes through vocal folds, making a sound like h. ”aspiration” )
b, d ,g (there is no aspiration and voicing continues)
Difference in the initial positions of p, t, k&b, d, g
Aspiration
In initial position b , d ,g cannot be preceded by any consonant
In initial position p , t ,k can be preceded by s and in such a situation p , t ,k will be un aspirated (spy, store, ski)
Medial position (v c v)
• We can say that a medial plosive may have the characteristics either of final or of initial plosives
Final position (v c)
In final position b , d ,g have little voicing and if there is voicing it is at the beginning of compression phase.
In final position p , t , k are obviously voiceless.
In final positions the plosion following the release of p,t,k&b,d,g is very weak and often not audible.
In final positions the vowels preceding p,t,k are much shorter. The shortening effect of p, t, k is most noticeable when the vowel is a long vowel or a diphthong.
Remarque :
Note the length difference in vowel
Mate | Made |
|---|---|
leak | league |
hurt | heard |

Remarque : Aspiration
• The phenomenon in which a small “puff of air” escapes through the vocal folds after the release phase. It is transcribed as [ Ch].
1- Voiceless plosive + a vowel sound → aspirated. | 2- /s/ + Voiceless plosive → unaspirated. | 3- Voiceless plosives in final position → unaspirated. |
|---|---|---|
/p/ pen → /pen/ → [phen] /t/ ten → /ten/ → [then] /k/ cat → /kæt/ → [khæt] | /p/ spy → /spaı/ → [spaı] /t/ stay → /steı/ → [steı] /k/ sky → /skaı/ → [skaı] | /p/ stop → /stɒp/ → [stɒp] /t/ start→ /start/ → [start] /k/ take → /teık/ → [teık] |

Complément :
you can also download additional exercises