consonants
Conseil : IPA chart
Before you start it is important to review IPA symbols
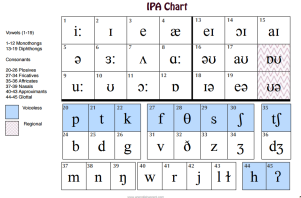
Définition : what is a consonant ?
A speech sound produced with air stream impeded, constricted, diverted, or obstructed.
Classification system for consonants
place, manner, and voicing
Place (also called place of articulation): Where is the breath stream impeded, constricted, diverted, or obstructed? For example:
lips, teeth, alveolar ridge, palate, velum, ...
Manner:How is the breath stream impeded, constricted, diverted, or obstructed? For example:
stop or plosive: complete obstruction of air stream :[b], [d], [g], [p], [t], [k]
fricative: air passed thru a narrow channel, creating turbulence.[ᶴ] (as in “shoe”), [ᶞ], (as in “this”).
nasal:air stream redirected through the nasal cavity: [m], [n], [ŋ] (as in “sing”)
affricate: complete obstruction of air stream followed by fricative release.[tʃ] (as in “choke”), [dʒ] (as in “joke”)
approximants:consonants that are almost like vowels[r] [l] [w] [j] (as in “yellow”)
Voicing : Are the vocal folds vibrating?
Yes Voiced
No Unvoiced/Voiceless
English has many pairs of consonants that are identical in all other ways except for voicing.
Some examples:
[b]-[p], [d]-[t], [g]-[k], [z]-[s], [ʒ]-[ʃ], [v]-[f], [ð]-[θ]
These are called voiced-voiceless cognates.






